The 100 Most Influential Books Ever Written
This is one of the 273 lists we use to generate our main The Greatest Books list.
-
Beyond Freedom and Dignity by B. F. Skinner
This book is a controversial exploration of human behavior that challenges the idea of free will and individual autonomy, arguing instead that human behavior is largely determined by environmental factors. The author proposes that societal issues such as overpopulation, war, and pollution can be addressed by using behavioral science to shape human actions. The book also criticizes traditional notions of punishment and reward, suggesting that these methods are ineffective in influencing behavior.
-
Quotations from Chairman Mao by Mao
This book is a collection of speeches and writings by the former leader of the People's Republic of China. It covers a wide range of topics including communism, revolution, class struggle, and the correct handling of contradictions among the people. The book was published with the intention of promoting the leader's ideology and was widely distributed during the Cultural Revolution. It was considered an essential guide to life and politics in China during this period.
-
The Feminine Mystique by Betty Friedan
This groundbreaking book is a sociological examination of the dissatisfaction felt by American housewives in the mid-20th century. The author argues that women are not naturally fulfilled by devoting their lives to homemaking and child-rearing, challenging the widely accepted belief of the era. It explores the idea of the "problem that has no name" - the widespread unhappiness of women in the 1950s and early 1960s. The book is considered one of the catalysts of the second-wave feminist movement.
-
The Structure of Scientific Revolutions by Thomas Kuhn
This influential book examines the history of science, focusing on the process of scientific revolutions. The author argues that scientific progress is not a linear, continuous accumulation of knowledge, but rather a series of peaceful interludes punctuated by intellectually violent revolutions. During these revolutions, known as paradigm shifts, the old scientific worldview is replaced by a new one. The book also popularized the term 'paradigm shift' and challenged the previously accepted view of science as a steadily progressive discipline.
-
Syntactic Structures by Noam Chomsky
This groundbreaking work introduces the theory of generative grammar, revolutionizing the study of linguistics by arguing that the structure of language is innate to the human mind rather than learned through social interaction. The book presents a new approach to the study of language, suggesting that linguistic structures are not simply mirrors of social realities but are governed by universal rules and principles. It also introduces the concept of transformational-generative grammar, a framework for describing the syntactic structures of language.
-
Philosophical Investigations by Ludwig Wittgenstein
This book is a seminal work in 20th-century philosophy, presenting a detailed critique of the notion that our language directly corresponds to reality. The author argues that the meaning of words is not inherent, but rather derives from their use within specific forms of life. The book also introduces the concept of language games, suggesting that our understanding of language is akin to learning the rules of a game. The author further explores the limits of language, the nature of understanding, and the relationship between public and private language.
-
Beelzebub's Tales to His Grandson by George Ivanovitch Gurdjieff
"Beelzebub's Tales to His Grandson" is a philosophical narrative that explores human nature and the universe. The story is told through the perspective of Beelzebub, a demon who shares tales of his experiences on Earth with his grandson. The book delves into deep philosophical and spiritual concepts, providing a critique of human behavior, societal norms, and the concept of enlightenment. It challenges readers to question their understanding of life, spirituality, and the nature of reality.
-
Nineteen Eighty Four by George Orwell
Set in a dystopian future, the novel presents a society under the total control of a totalitarian regime, led by the omnipresent Big Brother. The protagonist, a low-ranking member of 'the Party', begins to question the regime and falls in love with a woman, an act of rebellion in a world where independent thought, dissent, and love are prohibited. The novel explores themes of surveillance, censorship, and the manipulation of truth.
-
Cybernetics by Norbert Wiener
"Cybernetics" is a groundbreaking work that explores the complex relationship between humans and machines. The book delves into the field of cybernetics, a term coined by the author, which refers to the study of systems and processes that exist in mechanical, biological, and electronic domains. The author discusses the potential of machine learning, artificial intelligence, and computer technology, predicting their profound impact on society, economy, and human behavior. The book also highlights the ethical implications of these technological advancements.
-
The Second Sex by Simone de Beauvoir
This influential work explores the treatment and perception of women throughout history, arguing that women have been repressed and defined only in relation to men. The author presents a detailed analysis of women's roles in society, family, work, and in the creation of their own identities. She discusses the concept of 'the other' and how this has been used to suppress women, while also examining the biological, psychological, and societal impacts of this oppression. The book is a seminal text in feminist theory, challenging traditional notions of femininity and calling for equality and freedom for women.
-
The Road to Serfdom by Friedrich von Hayek
"The Road to Serfdom" is a classic work of political philosophy and economics that argues against the concept of socialism and centralized economic planning. The author asserts that such systems inevitably lead to totalitarianism, infringing upon individual liberties and stifling innovation. The book further posits that only through free-market capitalism can societies maintain political and economic freedom. The author also explores the dangers of government control over means of production, illustrating that it leads to a loss of personal freedoms and the rise of dictatorial regimes.
-
Being and Nothingness by Jean Paul Sartre
This philosophical work delves into the concept of existentialism and phenomenology, offering an in-depth analysis of human consciousness and existence. The author argues that we are all essentially free and responsible for our actions, and that we construct our own identities through our actions and interactions with others. The book also explores the idea of 'nothingness' and 'bad faith', suggesting that we often deny our freedom and hide from the responsibility of our actions, leading to a life of inauthenticity.
-
The General Theory of Employment, Interest and Money by John Maynard Keynes
This influential economic treatise presents a groundbreaking theory that challenges classical economics, asserting that aggregate demand, driven by public and private sector spending, is the primary factor influencing economic activity and employment levels. The book also introduces the concept of fiscal and monetary policies as tools to manage economic downturns, thus shaping the foundation of modern macroeconomics. It further critiques the idea that market economies would automatically provide full employment and argues for active government intervention to prevent economic recessions and depressions.
-
The Logic of Scientific Discovery by Karl Popper
This book is a significant work in the philosophy of science, proposing a methodology for scientific discovery that challenges traditional inductive reasoning. The author argues that scientific theories can never be proven definitively, but can only be corroborated or falsified through empirical testing. He introduces the concept of falsifiability as the key criterion for distinguishing scientific theories from non-scientific ones. The book also delves into the problems of induction, demarcation, and the relationship between theory and observation in scientific practice.
-
The Trial by Franz Kafka
The book revolves around a bank clerk who wakes one morning to find himself under arrest for an unspecified crime. Despite not being detained, he is subjected to the psychological torment of a bizarre and nightmarish judicial process. The story is a critique of bureaucracy, exploring themes of guilt, alienation and the inefficiency of the justice system.
-
I and Thou by Martin Buber
This philosophical work explores the concept of relationships and the nature of dialogue. The author suggests that human life finds its meaningfulness in relationships, which he divides into two categories: "I-It" and "I-Thou". The "I-It" relationship is characterized by a detached and objective perspective, while the "I-Thou" relationship involves a deep sense of connection and mutual existence. The book argues that modern society, with its emphasis on individualism and materialism, often neglects the "I-Thou" relationship, leading to a loss of genuine human connection.
-
Psychological Types by Carl Jung
"Psychological Types" is a seminal work that delves into the theory of psychological types, positing that there are fundamental differences in the way individuals perceive and interpret the world. The book introduces the concept of introverted and extroverted personality types, along with the four psychological functions of thinking, feeling, sensation, and intuition. The author argues that these personality types and functions shape our attitudes and behaviors, leading to different ways of interacting with and understanding the world around us.
-
The Mind and Society by Vilfredo Pareto
This book is a comprehensive analysis of the social and psychological processes that shape human behavior and society. The author introduces the concept of "residues" and "derivations" as the main drivers of human actions and societal change. He argues that residues, innate characteristics within individuals, are more stable and influential in shaping social phenomena, while derivations are the justifications or explanations people give for their actions. The book further delves into the classification of residues and the role they play in economics, politics, and social dynamics.
-
Relativity by Albert Einstein
This book is a comprehensive introduction to the theory of relativity written by the physicist who developed the theory. It covers both the special and general theories of relativity and provides an accessible explanation of the physics involved, including the nature of light, time, and gravity. The book also discusses the philosophical implications of relativity and its impact on our understanding of reality. Written for a general audience, it aims to make complex scientific concepts understandable to non-experts.
-
Pragmatism by William James
The book in question is a seminal work in the philosophical tradition of pragmatism, which argues that the truth of ideas is measured not by their correspondence to an objective reality, but by their practical effects and utility. The author challenges the notion of fixed, absolute truths, proposing instead that beliefs should be seen as tools for action and that their validity depends on their success in solving problems and guiding experiences. Through a series of lectures, the text explores the implications of this philosophy for various fields, including religion, metaphysics, and science, ultimately advocating for a more flexible, open-ended approach to thinking and a tolerance for diverse perspectives in the pursuit of knowledge and understanding.
-
The Interpretation of Dreams by Sigmund Freud
This groundbreaking work explores the theory that dreams are a reflection of the unconscious mind and a means of understanding our deepest desires, anxieties, and fantasies. The book delves into the symbolism of dreams and their connection to repressed thoughts and experiences, proposing that they are a form of wish fulfillment. The author also introduces the concept of "dream work," which transforms these unconscious thoughts into the content of dreams, and discusses various methods of dream interpretation.
-
Thus Spake Zarathustra by Friedrich Nietzsche
This philosophical novel explores the idea of the Übermensch, or "Overman," a superior human being who has achieved self-mastery and created personal meaning in life. The protagonist, Zarathustra, descends from his solitary life in the mountains to share his wisdom with humanity. Through a series of speeches and encounters, he challenges traditional beliefs about good, evil, truth, and religion, and advocates for the transcendence of man into a higher form of existence. The book is noted for its critique of morality, its poetic and often cryptic language, and its exploration of complex philosophical concepts.
-
Treatise on Electricity and Magnetism by James Clerk Maxwell
This seminal scientific work revolutionized the understanding of electricity and magnetism, providing a comprehensive mathematical framework for the interrelationship between these two forces. The book lays out the foundation of electromagnetic theory, introducing key concepts such as electromagnetic fields, electromagnetic waves and the speed of light. It also introduces the four fundamental equations, now named after the author, that describe how electric charges and currents create electric and magnetic fields.
-
War and Peace by Leo Tolstoy
Set in the backdrop of the Napoleonic era, the novel presents a panorama of Russian society and its descent into the chaos of war. It follows the interconnected lives of five aristocratic families, their struggles, romances, and personal journeys through the tumultuous period of history. The narrative explores themes of love, war, and the meaning of life, as it weaves together historical events with the personal stories of its characters.
-
Experiments on Plant Hybridization by Gregor Mendel
This seminal work in the field of genetics presents the results of a series of experiments conducted on pea plants, which led to the discovery of fundamental laws of inheritance. The author meticulously cross-bred different varieties of peas and meticulously recorded the traits of their offspring, leading to the formulation of the principles of segregation and independent assortment. These principles, which underpin modern genetics, explain how traits are passed from parents to offspring and how different traits are inherited independently of each other.
-
First Principles by Herbert Spencer
"First Principles" is a philosophical work that delves into the fundamental principles of the universe and human nature. It explores the idea of evolution and the law of organic progress, arguing that all entities, whether biological, psychological, or sociological, evolve from simple and homogeneous to complex and heterogeneous. The book also discusses the concept of 'survival of the fittest,' positing that this principle governs all transformations. It is a profound exploration of the interconnectedness of the universe and the natural laws that govern it.
-
On Liberty by John Stuart Mill
This influential philosophical work explores the concept of personal freedom and societal limits, arguing that individuals should have the right to act as they want, provided they do not harm others. The book elaborates on the nature and limits of the power that can be legitimately exercised by society over the individual, and champions individuality and nonconformity. It also discusses freedom of speech, asserting that all opinions should be openly expressed to prevent any single viewpoint from becoming dogma.
-
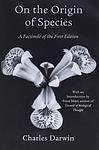
On the Origin of Species by Charles Darwin
This groundbreaking work presents the theory of evolution, asserting that species evolve over generations through a process of natural selection. The book provides a comprehensive explanation of how the diversity of life on Earth developed over millions of years from a common ancestry. It includes detailed observations and arguments to support the idea that species evolve by adapting to their environments, challenging the prevailing belief of the time that species were unchanging parts of a designed hierarchy.
-
Civil Disobedience by Henry David Thoreau
The book is a seminal work on the philosophy of non-violent resistance, advocating for individual freedom and the refusal to obey unjust laws. The author argues that individuals have a duty to prioritize their conscience over the dictates of laws and that governments are inherently prone to corruption and should not command absolute allegiance from their citizens. The book has greatly influenced many nonviolent resistance movements around the world, including those led by Gandhi and Martin Luther King Jr.
-
Communist Manifesto by Karl Marx, Friedrich Engels
This influential political pamphlet advocates for the abolition of private property, the rights of the proletariat, and the eventual establishment of a classless society. The authors argue that all of history is a record of class struggle, culminating in the conflict between the bourgeoisie, who control the means of production, and the proletariat, who provide the labor. They predict that this struggle will result in a revolution, leading to a society where property and wealth are communally controlled.
-
Either Or by Soren Kierkegaard
"Either Or" is a philosophical work that explores the concept of existentialism through the lens of two contrasting life views: the aesthetic and the ethical. The aesthetic life is characterized by immediate pleasure and enjoyment, while the ethical life is defined by moral duty and responsibility. The book presents these two perspectives through the fictional letters of two characters, ultimately arguing for the superiority of the ethical life. However, it also suggests that a truly fulfilled life must find a balance between the two.
-
On War by Carl Von Clausewitz
This book is a comprehensive analysis of warfare, written by a Prussian military theorist. It discusses the philosophical aspects of war, such as its political nature and purpose, as well as its practical aspects, such as strategy and tactics. The author argues that war is an extension of politics by other means and that its ultimate objective is to compel the enemy to fulfill our will. He also introduces the concept of "friction" in war, which refers to the unpredictable factors that can affect the outcome of military operations.
-
The Course in Positive Philosophy by Auguste Comte
"The Course in Positive Philosophy" is a philosophical work that introduces and elaborates on the concept of positivism, a belief system that emphasizes empirical science and factual knowledge. The author argues that society has passed through three stages: theological, metaphysical, and positive, with the positive stage being the most advanced and accurate. He asserts that all knowledge must come from observable phenomena and scientific inquiry, rejecting metaphysics and theology. The book is a cornerstone of modern sociology and philosophy, influencing many later thinkers.
-
Don Quixote by Miguel de Cervantes
This classic novel follows the adventures of a man who, driven mad by reading too many chivalric romances, decides to become a knight-errant and roam the world righting wrongs under the name Don Quixote. Accompanied by his loyal squire, Sancho Panza, he battles windmills he believes to be giants and champions the virtuous lady Dulcinea, who is in reality a simple peasant girl. The book is a richly layered critique of the popular literature of Cervantes' time and a profound exploration of reality and illusion, madness and sanity.
-
Pilgrim's Progress by John Bunyan
This Christian allegory follows a man named Christian on his journey from his hometown, the "City of Destruction," to the "Celestial City" on Mount Zion. Christian faces numerous obstacles and temptations along the way, including the Slough of Despond, Vanity Fair, and the Valley of the Shadow of Death. The narrative serves as a metaphor for the believer's journey from sin and despair to salvation and eternal life.
-
Leviathan by Thomas Hobbes
"Leviathan" is a seminal work of political philosophy that presents an argument for a social contract and rule by an absolute sovereign. The author argues that civil peace and social unity are best achieved by the establishment of a commonwealth through social contract. He suggests that without a strong, central authority to impose law and order, society would descend into a state of nature, characterized by perpetual war and chaos. The book is divided into four parts: Of Man, Of Commonwealth, Of a Christian Commonwealth, and Of the Kingdom of Darkness.
-
Essays by Michel de Montaigne
This collection of essays explores a wide range of topics such as solitude, cannibals, the power of the imagination, the education of children, and the nature of friendship. The author employs a unique and personal approach to philosophy, using anecdotes and personal reflections to illustrate his points. The essays provide a profound insight into human nature and condition, and are considered a significant contribution to both literature and philosophy.
-
The Prince by Niccolo Machiavelli
This classic work of political philosophy provides a pragmatic guide on political leadership and power, arguing that leaders must do whatever necessary to maintain authority and protect their states, even if it means compromising morality and ethics. The book explores various types of principalities, military affairs, the conduct of great leaders, and the virtues a prince should possess. It is known for its controversial thesis, which suggests that the ends justify the means in politics.
-
Gargantua and Pantagruel by Francois Rabelais
"Gargantua and Pantagruel" is a satirical and humorous tale of two giants, Gargantua and his son Pantagruel. The narrative is filled with bawdy humor, wordplay, and grotesque and exaggerated characters, reflecting the realities of 16th-century France. The book is also known for its profound insights on education, religion, and politics, often criticizing the corruption and hypocrisy of the powerful. The novel is a rich blend of fantasy, comedy, and philosophical discourse, making it a classic of Renaissance literature.
-
The Divine Comedy by Dante Alighieri
In this epic poem, the protagonist embarks on an extraordinary journey through Hell (Inferno), Purgatory (Purgatorio), and Paradise (Paradiso). Guided by the ancient Roman poet Virgil and his beloved Beatrice, he encounters various historical and mythological figures in each realm, witnessing the eternal consequences of earthly sins and virtues. The journey serves as an allegory for the soul's progression towards God, offering profound insights into the nature of good and evil, free will, and divine justice.
-
Confessions by Augustine
"Confessions" is an autobiographical work by a renowned theologian, in which he outlines his sinful youth and his conversion to Christianity. It is written in the form of a long, introspective prayer directed to God, exploring the author's spiritual journey and deep philosophical ponderings. The book is renowned for its eloquent and deeply personal exploration of faith, making it a cornerstone of Christian theology and Western literature.
-
The Iliad by Homer
This epic poem focuses on the final weeks of the Trojan War, a conflict between the city of Troy and the Greek city-states. The story explores themes of war, honor, wrath, and divine intervention, with a particular focus on the Greek hero Achilles, whose anger and refusal to fight have devastating consequences. The narrative also delves into the lives of the gods, their relationships with humans, and their influence on the course of events.
-
The Odyssey by Homer
This epic poem follows the Greek hero Odysseus on his journey home after the fall of Troy. It takes Odysseus ten years to reach Ithaca after the ten-year Trojan War. Along the way, he encounters many obstacles including mythical creatures, divine beings, and natural disasters. Meanwhile, back in Ithaca, his wife Penelope and son Telemachus fend off suitors vying for Penelope's hand in marriage, believing Odysseus to be dead. The story concludes with Odysseus's return, his slaughter of the suitors, and his reunion with his family.
-
The Republic by Plato
"The Republic" is a philosophical text that explores the concepts of justice, order, and character within the context of a just city-state and a just individual. It presents the idea of a utopian society ruled by philosopher-kings, who are the most wise and just. The dialogue also delves into theories of education, the nature of reality, and the role of the philosopher in society. It is a fundamental work in Western philosophy and political theory.
-
The History of the Peloponnesian War by Thucydides
This book is a historical account of the Peloponnesian War between the city-states of Athens and Sparta in ancient Greece. The author, an Athenian general, provides a detailed narrative of the war, its causes, and its consequences, offering valuable insights into the political and social dynamics of the time. The work is considered a pioneering piece in the field of history due to its rigorous methodology and critical analysis of events.
-
The Aeneid by Virgil
This epic poem tells the story of Aeneas, a Trojan who travels to Italy, where he becomes the ancestor of the Romans. It includes a series of prophecies about Rome's future and the deeds of heroic individuals, and is divided into two sections, the first illustrating the hero's journey and the second detailing the wars and battles that ensue as Aeneas attempts to establish a new home in Italy. The narrative is deeply imbued with themes of duty, fate, and divine intervention.
-
I Ching by China
This ancient Chinese text is a divination system and book of wisdom. It provides guidance for moral and ethical decisions through 64 hexagrams, which are six-line figures made up of broken and unbroken lines. Each hexagram represents a specific situation or state of affairs, and the text provides interpretations and advice for each. The book has been used for centuries as a tool for decision-making, prediction, and gaining deeper understanding of situations and relationships.
-
The Hebrew Bible by Jewish scripture
This book is a comprehensive collection of Jewish scriptures, also known as the Hebrew Bible or Tanakh, which is divided into three sections: the Torah (Pentateuch), the Nevi'im (Prophets), and the Ketuvim (Writings). It includes historical accounts, laws, ethical guidelines, songs, prayers, wisdom literature, and prophecies, providing the religious, moral, and social foundations for Judaism and, by extension, Christianity and Islam. The book is considered sacred and authoritative by Jews worldwide.
-
Upanishads by Hindu scripture
The book is a comprehensive compilation of ancient Hindu scriptures known as the Upanishads, which are fundamental to understanding the core philosophies of Hinduism. The text delves into profound spiritual teachings and philosophical dialogues about the nature of reality, the self, and the universe, providing invaluable insights into concepts such as karma, reincarnation, moksha, and the ultimate truth of existence. It serves as a guide to spiritual enlightenment and self-realization, offering timeless wisdom for introspection and personal growth.
-
Tao Te Ching by Lao Tsu
This ancient text is a fundamental guide to the philosophy of Taoism, offering wisdom on how to live a balanced, virtuous life in harmony with the natural world and the Tao, the source of all existence. The book explores themes such as simplicity, humility, and non-aggression, emphasizing the importance of understanding and aligning oneself with the Tao. It provides guidance on leadership, personal growth, and spiritual enlightenment, advocating for a life of peace, contemplation, and connection with the universe.
-
Avesta by Zoroastrian scripture
"Avesta" is a sacred text of Zoroastrianism, an ancient Persian religion predating Islam. The book contains the teachings of Zoroaster (Zarathustra), the prophet and founder of Zoroastrianism. It includes hymns, rituals, and legal and ethical codes, all intended to guide followers in their spiritual journey. The text also provides insights into the history, culture, and philosophical concepts of the Zoroastrian faith, including the dualistic cosmology of good and evil and the role of free will.
-
Analects by Confucius
The Analects is a collection of sayings and teachings attributed to the Chinese philosopher Confucius and his disciples. The book emphasizes the importance of personal and societal morality, filial piety, and the cultivation of knowledge and virtue. Confucius stresses the importance of leading by example and treating others with respect and kindness. The Analects has had a profound impact on Chinese culture and philosophy, and its teachings continue to be studied and applied today.
-
Hippocratic Corpus by Hippocrates
The "Hippocratic Corpus" is a collection of around 70 early medical works from ancient Greece, written in Ionic Greek. The texts are of varying content and length, covering a wide range of medical topics, including clinical descriptions of disease, surgical procedures, medical ethics, and philosophical reflections. Although traditionally attributed to Hippocrates, modern scholars believe that many of the works were not written by him and instead represent the work of several different authors over several decades. Despite this, the collection remains an invaluable resource for understanding the beginnings of Western medicine.
-
Corpus Aristotelicum by Aristotle
The "Corpus Aristotelicum" is a collection of texts by an ancient Greek philosopher, providing an extensive exploration of numerous fields of knowledge, such as metaphysics, ethics, logic, politics, biology, and poetry. These works have been instrumental in shaping Western philosophy and have had a profound influence on a wide range of subjects, including science, theology, and politics. The collection is known for its systematic and logical approach, and for its groundbreaking ideas that continue to stimulate intellectual discourse.
-
The Histories of Herodotus by Herodotus
"The Histories of Herodotus" is an ancient text that provides a comprehensive account of the Greco-Persian Wars. It is often considered the first work of history in Western literature. The author, often referred to as the 'Father of History', provides a narrative that not only discusses the conflicts between the Greeks and Persians, but also delves into the customs, geography, and history of each civilization. This detailed and pioneering work has greatly contributed to our understanding of the ancient world.
-
Euclid's Elements by Euclid
This book is a comprehensive collection of definitions, postulates, propositions, and mathematical proofs written by an ancient Greek mathematician. It is considered one of the most influential works in the history of mathematics, serving as the main textbook for teaching mathematics, especially geometry, from the time of its publication until the late 19th or early 20th century. The book covers topics such as plane geometry, proportion in general, the properties of numbers, incommensurable magnitudes, and solid geometry.
-
Dhammapada by Unknown
The Dhammapada is a revered text in Theravada Buddhism, containing 423 verses divided into 26 chapters. It provides a comprehensive guide to the Buddha's teachings, focusing on ethics, meditation, wisdom, and the path to nirvana. The verses are intended to be practical and applicable to everyday life, offering guidance on how to live a life of compassion, mindfulness, and wisdom. The text is considered one of the most accessible introductions to Buddhist philosophy and practice.
-
De Rerum Natura by Lucretius
"De Rerum Natura" is a long didactic poem written in the first century BC, which explores Epicurean philosophy and the nature of the universe. The text delves into topics such as the nature of the gods, the atomic structure of the universe, human sensation and thought, and the fear of death. The author argues that understanding the physical world can free humans from superstition and fear, leading to peace of mind and true happiness.
-
Allegorical Expositions of the Holy Laws by Philo of Alexandria
This book is a comprehensive examination of the Jewish laws as interpreted through the lens of Hellenistic philosophy. The author uses allegory to explain the significance and deeper meanings behind these laws, drawing on both Jewish and Greek philosophical traditions. The text serves as an exploration of morality, ethics, and religious observance, offering readers a unique perspective on Jewish law and its intersection with broader philosophical concepts.
-
Parallel Lives by Plutarch
"Parallel Lives" is a collection of biographies of famous Greek and Roman figures, written in pairs to draw comparisons between their lives. The work explores the influence of character on the lives and destinies of these historical figures. The biographies are not only a record of the lives of these individuals, but also provide insight into the times in which they lived, offering a unique perspective on the history and culture of the ancient world.
-
Annals by Cornelius Tacitus
"Annals" is a historical work that provides a comprehensive account of the Roman Empire from the reign of Tiberius in 14 AD to the death of Nero in 68 AD. The author, a senator and historian of the Roman Empire, explores the inner workings of Roman politics, military campaigns, and social culture during this period. The book offers an in-depth look at the political machinations, power struggles, and the moral decay of the Roman elite, providing a critical perspective on the Roman emperors and their rule.
-
Gospel of Truth by Valentinus
"Gospel of Truth" is a theological text that offers a unique interpretation of Christian doctrine from the perspective of Valentinian Gnosticism. The text explores the Gnostic view of Jesus Christ and His teachings, focusing on the concepts of knowledge, truth, and salvation. It delves into the idea of the spiritual realm, the divine Father, and the fall and redemption of mankind, presenting an alternative perspective to mainstream Christian thought.
-
Meditations by Marcus Aurelius
"Meditations" is a collection of personal writings by a Roman Emperor, providing deep insights into Stoic philosophy. The book is a series of introspective reflections on how to deal with life's challenges with wisdom, integrity, self-discipline, and benevolent affection for all mankind. It serves as a manual for self-improvement and moral guidance, emphasizing the importance of accepting things outside of one's control and maintaining a tranquil mind amidst adversity.
-
Outlines of Pyrrhonism by Sextus Empiricus
"Outlines of Pyrrhonism" is a philosophical text that delves into the teachings of Pyrrho, a Greek philosopher known for his skepticism. The book explores the concept of skepticism as a pathway to "ataraxia" (tranquility), arguing that suspending judgment leads to a state of mental peace. It presents Pyrrhonism as a philosophy that encourages the suspension of judgment about the truth of beliefs in order to achieve this tranquility. The text also provides a detailed comparison of Pyrrhonism with other philosophical schools of thought, such as Stoicism and Epicureanism.
-
Enneads by Plotinus
"Enneads" is a collection of 54 philosophical treatises by Plotinus, a prominent philosopher of the ancient world. The work is a cornerstone of Neoplatonism, a school of Hellenistic philosophy that sought to reconcile Greek philosophy with religious mysticism. The book covers a wide range of topics, including the nature of reality, the self, the universe, and the divine. The author argues for the existence of a transcendent One from which all existence emanates, and that the goal of human life is to strive for unity with this divine principle.
-
The Quran by Unknown
This book is a compilation of the religious text of Islam, believed by Muslims to be a revelation from God. It is divided into chapters, which are then divided into verses. The text discusses various aspects of life and provides guidance on morality, ethics, law, and personal conduct. It also includes narratives of several prophets, their lives, and their interactions with their communities. The book is considered the ultimate source of spiritual guidance for Muslims worldwide.
-
The Guide for the Perplexed by Moses Maimonides
This philosophical work serves as a guide for people who are perplexed by apparent contradictions between the teachings of religion and the discoveries of science. It seeks to reconcile the philosophy of Aristotle with the teachings of Judaism, arguing that the two are not in conflict but rather complement each other. The book also discusses the nature of God, the creation of the world, and the principles of morality, offering a comprehensive exploration of faith, reason, and the complexities of human understanding.
-
Kabbalah by Unknown
This book provides an in-depth exploration of Kabbalah, a mystical Jewish tradition. It delves into its historical origins, core philosophies, and spiritual practices, giving readers a comprehensive understanding of its principles and teachings. The book also discusses the Kabbalah's influence on various aspects of Jewish culture and its relevance in the contemporary world.
-
Summa Theologica by Thomas Aquinas
This comprehensive text is a seminal work in the field of theology, written by a prominent medieval philosopher and theologian. The book is structured in a question-and-answer format, tackling complex philosophical and theological issues such as the existence of God, the nature of man, the purpose of life, and the intricacies of morality and ethics. It is one of the most influential works in Western thought, particularly in Christian theology and philosophy, and continues to be a vital reference in these fields.
-
The Praise of Folly by Erasmus
This satirical work is a critique of the practices of the Church and the wider social behavior of the time. Narrated by Folly, the female personification of foolishness, the book humorously criticizes various aspects of society such as superstitious religious practices, scholarly pedantry, and the excesses of the upper classes. The book is a bold critique of its time, using humor and irony to expose the follies of its society.
-
Three Treatises by Martin Luther
"Three Treatises" is a collection of seminal works by a prominent religious reformer, focusing on the need for religious reformation and critiquing the Roman Catholic Church's practices. The first treatise discusses the Christian's spiritual nobility and priesthood, arguing that faith alone, not church rituals or hierarchy, connects one to God. The second treatise criticizes the Roman Church's wealth, advocating for the abolition of private mass and the selling of indulgences. The third treatise, written as an open letter to the Christian nobility, calls for the reform of the Church by secular authorities.
-
Institutes of the Christian Religion by John Calvin
This book is a comprehensive introduction to Christian theology and doctrine, written during the Protestant Reformation. The text outlines the author's views on subjects such as the nature of God, the authority of scripture, original sin, and salvation through Christ. The book also provides a detailed examination of the Ten Commandments and the Apostles' Creed, while offering a critique of the Catholic Church and its practices. The author's interpretation of Christianity, as presented in this work, has had a significant influence on the development of Protestant theology, particularly within Reformed churches.
-
On the Revolutions of the Heavenly Spheres by Nicolaus Copernicus
This book presents the revolutionary astronomical model that places the sun, rather than the earth, at the center of the universe. The author challenges the geocentric model of the cosmos, which had been widely accepted since the time of Aristotle, and instead proposes a heliocentric system, where the planets orbit the sun. This revolutionary idea transformed the way we understand our place in the universe, paving the way for modern astronomy and science.
-
The Harmony of the Worlds by Johannes Kepler
"The Harmony of the Worlds" is a scientific text that presents the author's innovative and groundbreaking theories on planetary motion. The author proposes that the movements of the planets in our solar system are not random, but rather follow precise mathematical relationships, likening these celestial patterns to harmonious musical notes. The book is a fundamental work in the history of astronomy, and it has had a profound influence on our understanding of the universe and its laws.
-
Novum Organum by Francis Bacon
This book is a philosophical work that presents a new method of acquiring knowledge and understanding the natural world, rejecting the traditional methods of the time. The author argues that human understanding is hindered by certain 'idols' or false notions, and proposes an inductive, experimental method, known as the 'Baconian method', which involves gathering data, making observations, and conducting experiments to understand the world. This method is seen as a precursor to the modern scientific method.
-
Dialogue Concerning the Two Chief World Systems by Galileo
This scientific work presents a series of discussions between three characters, each representing a different perspective on the cosmological theories of the time. Throughout the dialogue, the characters debate the merits of the Ptolemaic geocentric system, which asserts that the Earth is the center of the universe, and the Copernican heliocentric system, which proposes that the Sun is the center. The author uses these discussions to subtly argue in favor of the Copernican system, challenging the traditional religious and scientific beliefs of his time.
-
Discourse on Method by Rene Descartes
The book is a philosophical and autobiographical treatise that introduces a new form of scientific and philosophical method, which emphasizes on doubt and systematic questioning as the primary means to achieve knowledge. The author argues that by doubting everything, one can then rebuild knowledge, piece by piece, on a more solid foundation. This method is applied to a wide range of topics, including God's existence, the nature of the human mind and body, and the acquisition of knowledge.
-
Works of Gottfried Wilhelm Leibniz by Gottfried Wilhelm Leibniz
This book is a comprehensive collection of the philosophical, scientific, and mathematical works of a renowned 17th-century polymath. It includes his groundbreaking ideas in the fields of calculus, metaphysics, logic, and theology, as well as his correspondence with other notable intellectuals of his time. The compilation provides an in-depth look into his innovative concepts like the principle of sufficient reason, pre-established harmony, and monadology, offering a profound understanding of his significant contributions to the Age of Enlightenment.
-
Pensées by Blaise Pascal
"Pensées" is a collection of philosophical and theological thoughts and ideas by a renowned French mathematician and physicist. The book delves into various aspects of human existence, exploring the nature of faith, reason, and the human condition. It also presents arguments for the existence of God, including the famous wager argument. The book is known for its profound insights into the human experience and its exploration of the complexities of belief and doubt.
-
Ethics by Baruch de Spinoza
"Ethics" is a philosophical work that explores complex ideas about God, the universe, human emotions, and the path to enlightenment. The book outlines a metaphysical, epistemological, and ethical system in which God and the universe are one and the same, rejecting traditional notions of a personal deity and asserting that understanding the natural world leads to peace of mind and happiness. The work delves into the nature of the human mind and its emotions, advocating for the pursuit of reason and knowledge to achieve a calm, enlightened state.
-
Principia Mathematica by Isaac Newton
This seminal work is a comprehensive exploration of classical physics, laying the groundwork for much of modern science. The author presents his three laws of motion and law of universal gravitation, effectively bridging the gap between the abstract world of mathematics and real-world phenomena. The book also delves into the principles of calculus, a mathematical discipline the author significantly developed. This work has had a profound influence on the scientific understanding of the physical universe.
-
An Essay Concerning Human Understanding by John Locke
This philosophical work explores the concept of human understanding, proposing that all knowledge is derived from experience. The author argues against innate ideas, suggesting instead that the mind is a blank slate at birth, filled over time through sensory and reflective experiences. The book covers a wide range of topics, including language, memory, identity, and the limits of human knowledge, and is considered a foundational text in empiricism.
-
A Treatise Concerning the Principles of Human Knowledge by George Berkeley
This philosophical work challenges the idea of materialism, arguing that objects only exist as a perception of the mind. The author asserts that we can only directly know sensations and ideas of objects, not the objects themselves. He also discusses the role of God, suggesting that our perceptions are dependent on the will of a higher power. The text is a significant contribution to the field of metaphysics and epistemology, offering a unique perspective on the nature of human knowledge and perception.
-
The New Science by Giambattista Vico
"The New Science" is a groundbreaking philosophical work that proposes a new approach to the study of society, history, and the nature of human behavior. The author argues that human beings are the creators of their own history, culture, and society, and that they can therefore understand these phenomena in a way that they cannot understand the natural world. He also introduces the concept of a cyclical theory of history, where societies rise, develop, and eventually decline, only to rise again in a different form. The book has had a profound influence on a range of fields, including anthropology, sociology, and history.
-
A Treatise of Human Nature by David Hume
This philosophical work delves into the understanding of human nature, focusing on the mind, emotions, and morality. The author argues that all of our thoughts and ideas are derived from our senses and experiences, rejecting the idea of innate ideas. He also debates the nature of causality, the existence of the self, and the basis of moral judgments. The work is a comprehensive exploration of empiricism, skepticism, and naturalism.
-
Encyclopédie by Denis Diderot
This comprehensive work is a pioneering encyclopedia that aimed to present all the world's knowledge in a systematic and accessible way. It covers a wide range of topics including arts, sciences, crafts, professions, and technology. The book is also notable for its radical and enlightenment ideas, challenging traditional institutions and advocating for freedom of thought. It played a significant role in shaping the intellectual landscape of the 18th century and beyond.
-
A Dictionary of the English Language by Samuel Johnson
This comprehensive work is an extensive dictionary of the English language, providing detailed definitions, etymology, and usage examples for a wide range of words. It was one of the earliest dictionaries to approach language in this systematic and scholarly way, and it played a significant role in standardizing English spelling and usage. This dictionary is not only a linguistic resource but also a reflection of 18th century intellectual life, as it includes numerous quotations from notable authors and thinkers of the time.
-
Candide by Voltaire
"Candide" is a satirical novel that follows the adventures of a young man, Candide, who is living a sheltered life in an Edenic paradise and being indoctrinated with Leibnizian optimism by his mentor. When he is expelled from the paradise for kissing a baron's daughter, he embarks on a journey around the world, witnessing the horrors of war, natural disasters, and human cruelty. Throughout his journey, Candide maintains his optimistic philosophy, despite the constant hardships he faces, ultimately concluding that one must cultivate their own garden, a metaphor for taking control of one's own destiny.
-
Common Sense by Thomas Paine
This influential pamphlet, published in 1776, played a crucial role in persuading the colonists of the Thirteen Colonies to declare independence from Britain. It argues for the democratic system of government, criticizes monarchy and hereditary succession, and advocates for the inherent rights and freedoms of individuals. The text uses plain language to make complex political ideas accessible to the average citizen, promoting the idea that the colonies have a right to be an independent nation.
-
The Wealth of Nations by Adam Smith
This influential economic book presents a groundbreaking theory that argues for free market economies. The author posits that individuals acting in their own self-interest within a system of natural liberty will result in societal benefit, a concept often referred to as the "invisible hand" theory. The book also critiques mercantilism and explores concepts such as the division of labor, productivity, and free markets. It is widely considered one of the foundational texts in the field of economics.
-
The Decline and Fall of the Roman Empire by Edward Gibbon
This historical work provides a comprehensive perspective on the fall of the Roman Empire, examining its decline from the height of its power in the second century A.D. through the fall of Constantinople in 1453. The author meticulously chronicles the empire's deterioration due to a variety of factors, including moral decay, economic crisis, military incompetence, barbarian invasions, and internal power struggles, while also offering insightful commentary on the broader implications for Western civilization.
-
Critique of Pure Reason by Immanuel Kant
This philosophical work delves into the nature and limits of human knowledge, proposing that while our knowledge begins with experience, it doesn't necessarily arise out of experience. The author argues that pure reason itself has the ability to contribute to our knowledge and understanding of the universe. He further explores the concept of metaphysics, asserting that while it is possible, it is also severely limited by the human mind's ability to comprehend it.
-
The Confessions of Jean-Jacques Rousseau by Jean-Jacques Rousseau
"The Confessions of Jean-Jacques Rousseau" is an autobiographical work by a prominent philosopher of the Enlightenment era, who candidly shares his life story, from his humble beginnings in Geneva to his later years in exile. The book delves into his personal struggles, his intellectual journey, and his relationships, all while exploring his philosophical ideas on education, politics, and morality. The author's introspective narrative provides a unique perspective on his life and times, making it a seminal work in the history of autobiography.
-
Reflections on the Revolution in France by Edmund Burke
This book is a political pamphlet written in the 18th century, where the author criticizes the French Revolution, arguing that it has gone too far in its quest for radical change. He asserts that the revolutionaries, in their rejection of tradition and their embrace of abstract notions of liberty and equality, have overlooked the complexities of real social and political life. The author advocates for gradual, prudent reform rather than sudden, violent change and emphasizes the importance of tradition and inherited institutions.
-
A Vindication of the Rights of Woman by Mary Wollstonecraft
This influential work from the late 18th century argues passionately for the education and societal recognition of women. The author asserts that women are not naturally inferior to men, but appear to be only because they lack education. She suggests that both men and women should be treated as rational beings and imagines a social order founded on reason. The book is considered one of the earliest works of feminist philosophy.
-
Enquiry Concerning Political Justice by William Godwin
This book is a philosophical work that explores the concept of political justice, arguing against the established political institutions and proposing a society based on reason and justice, where individuals are not coerced by laws but guided by their own sense of morality. The author criticizes institutions like monarchy, aristocracy, and even democracy, while advocating for a form of anarchy where people live in small, self-governing communities. The work is considered a foundational text in anarchist theory.
-
An Essay on the Principle of Population by Thomas Robert Malthus
This influential work explores the theory that population growth will always tend to outrun the food supply and that betterment of humankind is impossible without strict limits on reproduction. The author argues that poverty, disease, and starvation are all necessary to keep societies from moving beyond their means of subsistence. The book's grim outlook and controversial theories have sparked significant debate and criticism since its publication.
-
The World as Will and Idea by Arthur Schopenhauer
This philosophical work posits that the world is driven by a continually dissatisfied will, continually seeking satisfaction. The book is divided into four parts, with the first addressing the world as representation, the second detailing the world as will, the third discussing art and beauty as the only way to transcend the painful human condition, and the fourth discussing ethics and the ascetic ideal. The author argues that the will is the underlying reality of the world, beyond mere appearances, and that it is characterized by ceaseless striving and suffering.
-
First Folio by William Shakespeare
This collection is a compilation of 36 plays by a renowned English playwright, published seven years after his death. It includes comedies, histories, and tragedies, some of which had never been published before. Notable works in the compilation include "Macbeth," "Julius Caesar," "Twelfth Night," "The Tempest," and "As You Like It." The collection is considered one of the most influential books ever published in the English language, as it preserved many of the playwright's works that might have otherwise been lost.
-
Phenomenology of Mind by G. W. F. Hegel
This profound philosophical work delves into the evolution of consciousness, examining the stages it goes through from simple sensory awareness to the complexities of ethical life and self-awareness. The author argues that the mind does not exist in isolation, but rather develops through interpersonal relationships and societal interactions. The book also presents the concept of dialectical reasoning, suggesting that truth is not static but evolves over time through a process of thesis, antithesis, and synthesis.
Martin Seymour-Smith, 101 Books
The 100 Most Influential Books Ever Written: The History of Thought from Ancient Times to Today (1998) is a book of intellectual history written by Martin Seymour-Smith (1928–1998), a British poet, critic, and biographer.
Added about 10 years ago.
This list has a weight of 38%. To learn more about what this means please visit the Rankings page.
Here is a list of what is decreasing the importance of this list:
- Voters: 1 person voted
- List: criteria is not just "best/favorite"
- List: only covers mostly "Western Canon" books
If you think this is incorrect please e-mail us at contact@thegreatestbooks.org.